Table of Contents
What is Inter-networking? Explained with Real-World Examples
Imagine living in a world where your phone couldn't talk to your laptop, your company’s branch offices couldn’t share data, or cloud servers couldn’t connect across the globe. Sounds impossible today, right? That’s because of something called inter-networking.
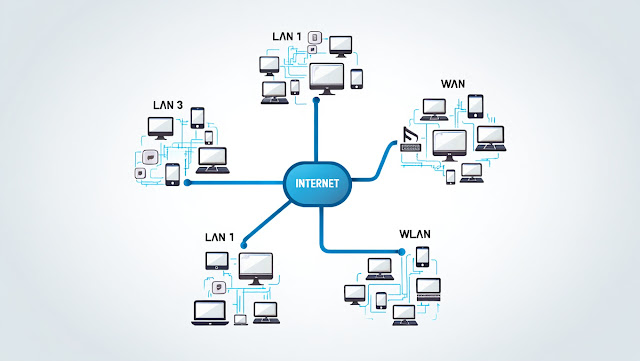
In simple terms, internetworking is the process of connecting multiple computer networks together to function as a single large network. It lets different systems communicate — even if they use different technologies.
Why Inter-networking Matters in Today’s World?
Whether you're making a WhatsApp call or transferring files between two branches of a company — inter-networking is working behind the scenes. It enables:
- Global Communication: From emails to video calls, all depend on interconnected networks.
- Cloud Access: Access Google Drive? That’s internetworking!
- Business Operations: Enterprises rely on private internetworks for real-time data sharing.
Fun Fact: There are over 5 billion internet users in 2025. That’s internetworking in action!
Types of Inter-networking Examples:
The Internet
The largest example of internetworking is the Internet. Billions of devices across the world — each from different networks — talk to each other seamlessly. That’s possible due to TCP/IP and routers.
Enterprise Networks
Large corporations use enterprise networks to connect multiple sites, data centers, and users. For example, Amazon's internal network connects warehouses, offices, and cloud servers globally.
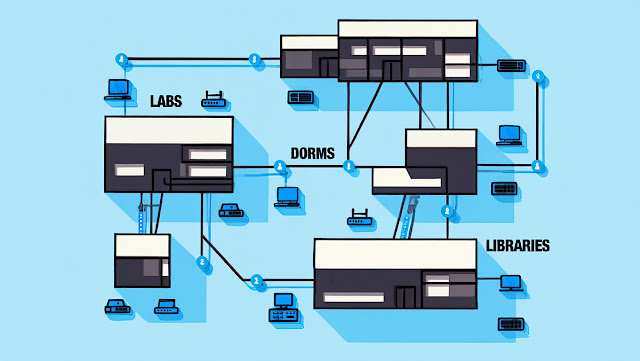
Campus Networks
A university campus has labs, dorms, and libraries — all connected in one network. That’s a campus internetwork. It connects LANs using switches and routers for seamless access.
Cloud Networking
Services like AWS or Google Cloud let businesses host apps and services. These rely on internetworking between physical data centers and virtual servers.
Home and Office Networks
Ever streamed Netflix while someone else joins Zoom from the same Wi-Fi? Your home router connects all devices into a local internetwork. Office routers do the same — just on a bigger scale.
Key Components of Inter-networking
- Routers: Direct traffic between networks
- Switches: Connect devices within a LAN
- Protocols: Like TCP/IP — they define how devices talk
- IP Addresses: Identify devices on the network
👉 Essential Networking Hardware Devices and Technologies: A Beginner-Friendly Guide (2025)
Future of Inter-networking
With new tech like IoT, 5G, and IPv6, internetworking is evolving fast. Smart homes, driverless cars, and smart cities will depend on high-speed, secure internetworks to function smoothly.
IPv6 allows more unique IP addresses than IPv4 — essential as billions more devices go online.
Conclusion
Internetworking is the invisible force connecting our digital world. Whether it's your smartwatch syncing with your phone or massive enterprise clouds, it’s all part of the same system. The more we depend on technology, the more crucial it becomes to understand how these networks operate together.
👍 If you found this helpful, read more about computer networking.
Keywords: what is internetworking, types of computer networks, internetworking examples, internetworking vs networking, enterprise network example


.webp)