What is a Computer Network? Components Of Computer Network (NIC, Switch, Cables and Connectors, Routers, Modems)
Have you ever paused for a second and wondered how that "Send" button on your messaging app actually delivers your words to someone sitting thousands of miles away — almost instantly?
In our everyday lives, we’re constantly connected — to our loved ones, to work, to entertainment. But behind this magical curtain of seamless communication lies an invisible but powerful structure known as a Computer Network.
Let’s be honest, we rarely think about what happens behind the scenes. But imagine life without Wi-Fi, without internet, without instant sharing of photos, documents, or video calls. Feels unsettling, right? That’s exactly why understanding the components of a computer network is more important than ever — whether you're a student, a professional, or simply a curious mind.
In this emotionally resonant and eye-opening post, we’re going to uncover what a computer network really is, and explore its essential components like NIC, Switch, Cables and Connectors, Routers, and Modems.
Table of Contents
- What is a Computer Network?
- Network Interface Card (NIC)
- Switches in Networking
- Cables and Connectors
- Routers
- Modems
- Pros and Cons Table of Components
- Conclusion: Why Networks Are Our Digital Lifelines
- FAQs About Computer Network Components
What is a Computer Network?
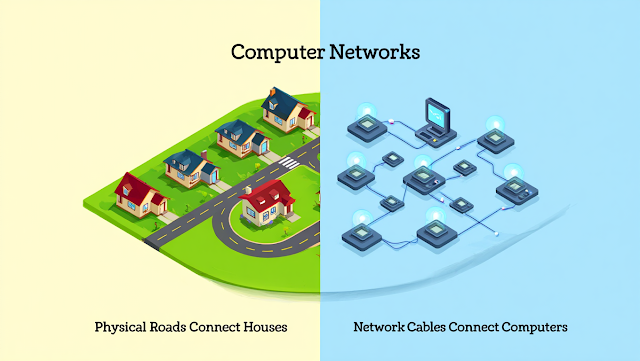
Imagine a city where people live in different houses, and each house is filled with valuable knowledge and resources. But none of these people can communicate unless roads connect them. A computer network is exactly like those roads — it connects different computers (houses) and enables them to share data, resources, and communication efficiently.
In simpler terms, a computer network is a system where multiple computing devices are linked together to exchange data and share resources like printers, files, and internet access.
Computer networks can be as small as two connected laptops (called Personal Area Network - PAN) or as massive as the global internet (Wide Area Network - WAN). And they work silently in the background of almost every digital interaction you experience.
Network Interface Card (NIC)
What is a NIC?
A Network Interface Card (NIC) is the heart of any network-enabled computer. It's the piece of hardware that physically connects a computer to the network via a cable or wirelessly.
It acts like the translator between your computer’s data and the signals used on the network.
Real-Life Analogy:
Think of a NIC as a phone’s SIM card — it gives your device a unique identity and connects it to a broader communication system.
Pros:
- Enables communication with other devices.
- Supports both wired and wireless connections.
- Easy to upgrade and replace.
Cons:
- Can be damaged or outdated with time.
- Varies in speed and compatibility.
Switches in Networking
What is a Switch?
A Network Switch is like the traffic police of your network. It decides which device should get which piece of data — intelligently directing traffic to avoid chaos.
It connects multiple devices in a Local Area Network (LAN) and uses MAC addresses to forward data only to the intended device.
Real-Life Analogy:
Imagine you're in a post office. The switch is the clerk who ensures every letter goes into the correct mailbox.
Pros:
- Reduces unnecessary data traffic.
- Improves network efficiency.
- Secure internal communication.
Cons:
- More expensive than hubs.
- Configuration can be complex for large networks.
Cables and Connectors
What are They?
Cables and connectors are the physical medium that carries data from one device to another. Common types include Ethernet (Cat5e, Cat6), coaxial, and fiber optic cables.
Connectors, like RJ45, attach the cable to network ports.
Real-Life Analogy:
They’re like the highways and bridges that connect different cities in a country.
Pros:
- High data transfer rates.
- Reliable and secure transmission.
Cons:
- Limited by distance and physical damage.
- Installation can be costly in large areas.
Routers
What is a Router?
A Router connects different networks together. It routes data from your local network to other networks — like the internet.
It typically connects to a modem and then to other devices through wired or wireless signals.
Real-Life Analogy:
A router is like a border control officer — checking and directing every packet that leaves or enters your network.
Pros:
- Enables internet access.
- Provides firewall and security features.
- Supports multiple devices wirelessly.
Cons:
- Can be vulnerable to hacking if not secured.
- Limited range and speed depending on the model.
Modems
What is a Modem?
A Modem (Modulator-Demodulator) is the device that connects your local network to your Internet Service Provider (ISP). It converts digital signals to analog and vice versa.
Without a modem, you simply can’t access the internet via broadband or DSL connections.
Real-Life Analogy:
A modem is like a translator between two people speaking different languages — it makes sure your home network speaks the same language as your ISP.
Pros:
- Essential for internet access.
- Stable and consistent connectivity.
Cons:
- Needs to be compatible with your ISP.
- May require frequent reboots or upgrades.
Pros and Cons Table of Components
| Component | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| NIC | Enables device communication, Upgradable | Can be damaged, speed limitations |
| Switch | Efficient data routing, reduces traffic | Expensive, complex configuration |
| Cables & Connectors | High speed, secure | Prone to damage, distance limits |
| Router | Internet access, multi-device support | Security risks, range limits |
| Modem | Connects to ISP, stable connection | Compatibility issues, frequent reboots |
Conclusion: Why Networks Are Our Digital Lifelines
We often take technology for granted. But when you really pause to reflect, the role of computer networks is deeply personal and profoundly vital.
They connect people who are far apart. They support businesses, power education, and keep emergency services online. And in an era where remote work, online learning, and digital love stories have become part of our daily lives — networks are more than just cables and devices.
They are the invisible threads that hold our digital world together.
So the next time your video call connects without a glitch, or your download finishes in seconds, take a moment to appreciate the silent guardians working behind the scenes — the NICs, switches, cables, routers, and modems that make it all possible.
Want to learn more about how networking works behind the scenes? Explore our Networking section for more insightful posts!
FAQs About Computer Network Components
1. Is a modem and a router the same thing?
No, a modem connects you to the internet via your ISP, while a router distributes that internet connection to multiple devices.
2. What’s the difference between a switch and a hub?
A switch sends data only to the device it’s meant for, while a hub broadcasts it to all devices, causing unnecessary traffic.
3. Can I use a computer without a NIC?
Not for network-related tasks. NIC is essential for connecting your device to any network — wired or wireless.
4. Are cables still used in modern networks?
Absolutely! Wired connections using Ethernet are still preferred in many settings for speed and stability.
5. How can I secure my home network?
Use strong Wi-Fi passwords, keep your router firmware updated, and enable network firewalls.



.png)



